Shenzhen Smart Community Solution Case
The high-density residential area newly built in Shenzhen in 2024 has a permanent population of about 25000. In the early stages of the community, it faced multiple challenges: low property management efficiency, insufficient resident participation, frequent safety hazards (such as high-altitude littering and electric vehicles entering elevators), and prominent digital divide among the elderly. In response to the national policy of smart cities and modernization of grassroots governance, the community has joined forces with the government, technology companies, and resident representatives to launch the "Smart Community 2.0" construction plan, aiming to achieve "refined governance, humanized services, and diversified participation" through technological empowerment.
Solution and Implementation Path
1. Build a "one brain, multiple terminals" intelligent management platform
Core architecture: Establish a community "smart brain" with AI cloud computing center as the core, integrate IoT devices, government data, and residents' needs, and achieve cross departmental data exchange.
Functional modules:
Intelligent security: deploy high-altitude projectile monitoring cameras (accurately locate the source of the projectile and automatically retain evidence); Elevator obstruction system (detects automatic shutdown of electric vehicles).
Environmental management: Install PM2.5 sensors and an intelligent garbage classification system (with a point reward mechanism to enhance residents' participation in environmental protection).
Emergency response: Real time monitoring of fire escape occupancy, water leakage and other risks through the Internet of Things, automatic distribution of work orders to property personnel, and average processing time reduced to within 30 minutes.
2. Multi subject collaborative operation mode
Government enterprise cooperation: The government takes the lead in introducing technology service providers such as ZTE and Vanke Property, and adopts the PPP model to share construction costs, with enterprises responsible for later operation and maintenance.
Resident Participation: Developed the "Bright Neighborhood" app, which integrates functions such as repair reporting, discussion, and volunteer service. Residents can submit suggestions in real time and participate in community decision-making and voting, handling over 200 resident proposals.
Social organization linkage: Cooperate with professional social work organizations to carry out "digital aging adaptation" training, covering over 80% of elderly residents and reducing the threshold for using smart devices.
3. Green and intelligent integrated infrastructure
Energy saving system: Adopting ground source heat pump for centralized heating and cooling, combined with solar street lights and rainwater recovery system, energy consumption is reduced by 40%.
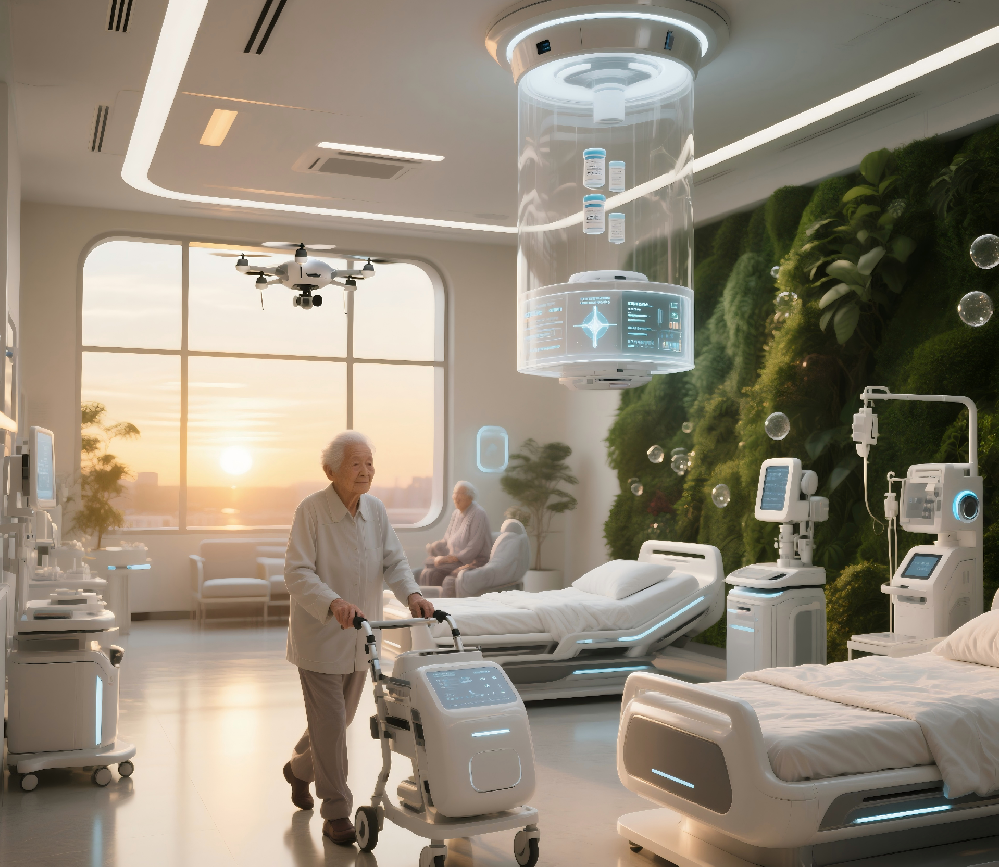
Smart Home Unit: Equipped with smart door locks and remote home appliance control modules as standard for each household, and linked with community platforms to achieve personalized services such as one click alarm and health monitoring.
4. AI empowers innovation in community services
Digital assistant "Guangming Xiaohui": developed based on a big language model, providing 24-hour policy consultation and service guidance, with a cumulative service of over 50000 times and an accuracy rate of over 95%.
Smart Elderly Care: Equip elderly people living alone with wearable devices to monitor their heart rate and location in real-time, and automatically notify their families and community grid members of any abnormal situations.
Implementation effectiveness
1. Improvement of governance efficiency
Reduce safety accidents by 60% and improve property work order processing efficiency by 70%.
Through the data sharing platform, cross departmental collaboration processing time has been reduced from 3 days to 4 hours.
2. Significant improvement in resident satisfaction
The utilization rate of digital services among the elderly population has increased from 15% to 65%, and the participation rate in community activities has increased by 50%.
In the third-party survey conducted in 2025, residents' satisfaction with the community environment reached 92%, ranking among the top in the city.
3. The emergence of sustainable ecology
The application of green technology reduces carbon emissions by about 1200 tons annually and has been awarded the title of "Guangdong Province Low Carbon Community Demonstration Site".
The proportion of social capital investment exceeds 40%, forming a replicable commercial operation model.
The three core strategies of the case:
Technology integration: Breaking information silos through AIoT and big data to achieve full scene coverage.
Humanized governance: guided by residents' needs, balancing technological applications with humanistic care.
Innovative model: Government, enterprises, and residents jointly govern to build a sustainable ecosystem.
This case provides a template for other communities to learn from, and in the future, it can further integrate cross community data linkage technology to promote the advancement of smart communities towards "digital real symbiosis".




